Major Cyber Security Threats in Telecom and Ways to Mitigate them
22-06-2022 Aesthetix

Communication networks must be dependable. The present extent, diversity, and complexity of cybersecurity threats are expanding dramatically. The increasing number of data transfers, legacy technology, signalling protocols, the expanding role of cloud technologies, and "outdated" DNS and DDoS attacks are among the most prevalent "bullets" that telcos must avoid daily. Let's focus on the most important of them.
1) DDoS:
Advanced distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks utilizing conventional network protocols and botnets comprising hacked mobile and IoT devices are prevalent. A DDoS is a Dedicated Denial of Service, which is an assault that disrupts regular traffic and, thus, denies service to the victim. This service outage might cause a business to incur severe financial losses.
DDoS assaults are brutal to prevent or defend against. Create a disaster recovery strategy in collaboration with your IT and cybersecurity professionals, and consider how you may respond to a DDoS attack. Due to the complexity of each organizational setting and how data is handled, there is no solution capable of preventing an attack.
2) DNS:
DNS (Domain Name Security) assaults continue to be a significant pain point for telecommunications companies. Worse, the cost of such attacks is increasing year by year. Cache poisoning, rebinding assaults, and domain lockups are the most common.
Reliable methods to prevent DNS assaults consist of proactive cyber resilience measures, such as identity management solutions for admin and server access. Similarly, you can augment firewalls with machine learning-driven policies.
3) IoT (Internet of Things):
How the Internet of Things (IoT) will affect the industry is one of the most critical obstacles facing Telco and Internet Service Providers (ISPs) in the current environment. The application of IoT to linked devices has exploded, providing more entry points in the process. Not all of these vulnerabilities are effectively fixed, exposing user, client, and company accounts.
The telecom business must use online data protection measures such as virtual private networks (VPNs), SIM-based authentication procedures, and identity management solutions. VPN establishes a safe connection to the internet by routing data traffic through an encrypted virtual tunnel. It masks the user's Internet Protocol (IP) address, safeguarding them from external threats.
Also Read: How AI And IoT Are Used To Monitor And Detect Leaks In Pipelines
4) Cloud security threats:
Some typical cloud security concerns are misconfiguration, data leaks, insider threats, lack of cloud security infrastructure and strategy, inadequate key management, and weak control planes.
It is essential to monitor employee cloud usage and apply precautions to prevent cloud data loss. In addition, risk can be reduced by controlling mobile devices and defining permissions for the company and user-owned endpoints, such as workstations, laptops, and cellphones.
5) Insider threats:
While some attacks in the telecom business are vindictive, many employees and insiders are unaware that they even pose a threat. Additionally, few individuals receive training on telecom security procedures. With as much as 30 percent of telecom employees working remotely, connections to insecure networks are at an all-time high.
In line with this, empirical research reveals that despite being aware of the hazards, people continue to connect to unsecured Wi-Fi networks, primarily for convenience. Unfortunately, a large number of programmes do not encrypt the data that their users send. Biometric security is a component of cloud-based authentication, a countermeasure to this issue. It safeguards your data regardless of where your users or workers connect.
6) Third-party risks:
Third parties such as suppliers, partners, email providers, service providers, web hosting, law firms, information management enterprises, and subcontractors might offer an attacker a backdoor into your critical infrastructure.
Maintaining the security of your company and the service providers in your industry might be difficult. Managed telecommunications security services are necessary for network-wide monitoring.
7) Terrorism and state actors:
Malicious actors can restrict the critical infrastructure's physical factors through remote intrusion and control the outcomes. They can collect vital information regarding intellectual property, trade agreements, and personal information. Since highly sophisticated threat groups carry them out, there is a strong probability that many successful telecom infrastructure breaches are never identified.
Always be careful of identity fraud to combat terrorist and state actor threats. Comprehensive solutions, such as premier identity proofing solutions, enable background check capabilities to validate identities and provide assurance for everyone in your system.
Conclusion
Telecom players have both an exciting and complicated period ahead. The sector is witnessing substantial alterations due to new assets such as IoT devices, leading to new income prospects and value streams.
To have robust and reliable telecom security mechanisms, you will need to convert from reactive security to proactive – one that relies on extensive monitoring and has predictive capabilities fueled by modern analytics and AI. Conduct through risk assessments for present systems, decentralize and automate the critical security requirements with appropriate tools and do even deeper checks for new technologies such as IoT and 5G.
View our updates
Our Blogs
Navigating Telecom Integration in Brownfield Infrastructure
Brownfield telecom integration upgrades live networks without service disruption. It modernises legacy systems, integrates 5G and fibre, and improves reliability, safety, and scalability. With a phased, structured approach, Aesthetix drives digital transformation while ensuring secure and continuous network performance.
 View Details
View Details

Key Engineering Challenges in Telecom Design for Hydrogen Plants
Telecom systems are vital to the safety, automation, and reliability of hydrogen plants in hazardous environments. This blog covers key telecom engineering challenges like ATEX compliance, network redundancy, and safety integration, and explains how Aesthetix delivers telecom solutions for hydrogen facilities.
 View Details
View Details

How Communication Networks Enhance Pipeline Safety and Prevent Disasters
Aesthetix is redefining pipeline safety with intelligent communication networks and advanced real-time monitoring solutions. By integrating telecom systems with cutting-edge sensing and analytics technologies, Aesthetix helps prevent pipeline disasters, ensuring safer, smarter, and more reliable energy operations worldwide.
 View Details
View Details

Pipeline Safety Challenges in Oil & Gas: How Technology Prevents Costly Leaks
Aesthetix offers custom pipeline safety solutions with advanced leak detection systems. Using a combination of AI, fiber optics, acoustic monitoring, and real-time data analytics, Aesthetix helps prevent costly leaks, and ensure full compliance with global and regional safety standards, safeguarding your operations and assets.
 View Details
View Details

How Integrated FPSO Telecom Enhances Emergency Response Capabilities
Aesthetix provides integrated FPSO telecom solutions, ensuring seamless communication, real-time data transmission, and automation for enhanced emergency response. With IoT integration and advanced technologies, Aesthetix supports offshore safety, operational efficiency, and resilience, driving innovation in offshore telecom.
 View Details
View Details

How Ergonomics Improves Decision-Making in High-Stress Environments
Discover how Aesthetix’s ergonomic solutions empower better decisions in high-stress environments. Reduce fatigue, boost focus, and enhance safety in oil rigs, control rooms, and beyond — creating smarter workspaces that keep minds sharp and performance at its peak. Elevate productivity with every task.
 View Details
View Details

Human Factor Engineering ROI: How Proper Design Reduces Operational Errors
At Aesthetix, we integrate Human Factors Engineering (HFE) into system design to minimize errors, enhance safety, and maximize operational efficiency. By blending cognitive and physical ergonomics, we create intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that reduce fatigue, improve decision-making, and prevent costly mistakes.
 View Details
View Details
685156448cd29.jpg)
When to consider a control room revamp: 5 Key Indicators
Transform your control room with Aesthetix's AI-driven, ergonomic solutions boost efficiency, safety & scalability for oil/gas, utilities & transport sectors. Featuring real-time analytics and modular designs to minimize downtime while future-proofing critical operations. Our customized solutions integrate seamlessly with your existing infrastructure for immediate performance improvements
 View Details
View Details
6821ef9f8971f.jpg)
Future of Control Room Design: Trends & Innovations
Explore the future of control room design with Aesthetix—leveraging AI, IoT, cloud computing, and advanced ergonomics for intelligent, sustainable, and secure operations. Tailored for UAE’s extreme climate & Vision 2030, our solutions enhance efficiency, safety, and operator well-being in industries like energy, smart cities, etc.
 View Details
View Details
67f7b130effe8.jpg)
Enhancing FPSO Operations with Advanced Telecom Systems
Advanced telecom systems are revolutionizing FPSO operations by enabling real-time communication, enhancing safety, and boosting efficiency in harsh offshore environments. Aesthetix delivers robust, integrated telecom solutions tailored for FPSOs, ensuring reliability, compliance, and seamless operations.
 View Details
View Details
67c1657c99568.jpg)
Cybersecurity in the Oil and Gas Sector
Explore key cybersecurity challenges in the oil and gas sector, real-world attacks, etc. Learn how Aesthetix enhances security with advanced threat detection and proactive defense strategies. Stay ahead of evolving threats with custom solutions tailored for the energy industry, ensuring operational resilience and compliance with global security standards.
 View Details
View Details
679b189aa5bb4.jpg)
Oil and Gas Sector: The Role of Telecom Technologies
Telecom technologies play a crucial role in transforming the oil and gas sector by enhancing communication, improving operational efficiency, and ensuring safety in remote locations. This blog explores how advanced telecom solutions, such as IoT, 5G, and satellite communications, are revolutionizing the industry, enabling real-time data exchange, automation, and seamless connectivity across offshore and onshore operations.
 View Details
View Details

What is Human Machine Interface (HMI) Analysis?
Discover how Human-Machine Interface (HMI) plays a pivotal role in modern manufacturing. This blog explores the essential functions of HMI, its components, and how it enhances productivity, safety, and troubleshooting. Learn about the various types of HMIs, their impact on industrial processes, and the future advancements shaping the way operators interact with machinery.
 View Details
View Details
673458f69fa05.webp)
Sustainability In The Oil And Gas Industry
Discover the top cybersecurity threats facing the oil and gas industry, including real-world attack examples and proven defense strategies. Learn how Aesthetix delivers cutting-edge solutions to safeguard critical infrastructure, ensure compliance, and mitigate risks in an evolving digital landscape.
 View Details
View Details

Why Do We Need to Use an Anti-Static Raised Floor?
Imagine the frustration of constantly experiencing electrostatic discharge (ESD) at your workplace, which is similar to the shock you get from stepping on a carpet and then touching a doorknob. Even tiny electrical pulses have the potential to cause operational disruptions in sensitive locations such as production facilities.
 View Details
View Details

What is a Working Environment Health Risk Assessment ?
Maintaining a safe workplace is not just an obligation; it's also a chance to enhance the working environment for your staff. How do you ensure the safety of your workplace? What all factors do you need to consider? This is where an environmental health risk assessment comes in.
 View Details
View Details

Why is Ergonomics Important?
Ergonomics is the study of people in the workplace. An ergonomist seeks to create or alter the workspace to fit the worker, rather than the other way around.
 View Details
View Details

Understanding ergonomics In Control Room Design
The fundamental principle of ergonomics centers on the optimization of workspaces, products, and systems to suit the needs of their users. It encompasses the design of environments for work, recreation, and fitness, with a paramount emphasis on promoting health and safety.
 View Details
View Details

Role of Telecom System Integration in Oil and Gas Industries
The telecommunication requirements of the oil and gas industry are significantly different from those of carriers or enterprises. The challenge for oil and gas companies lies in maximizing production while minimizing both capital and operational expenses. To achieve this goal, a reliable telecommunications network is essential. These networks, owned and maintained privately.
 View Details
View Details

How Do Industrial Ergonomics Improve Productivity?
Improving productivity is always top of mind for employers. They plan and implement various organizational changes that will boost productivity and enhance the safety of employees. Employers now understand the importance of taking care of the emotional well-being of their employees to keep them motivated and productive
 View Details
View Details

How Mining Automation Transforms the Mining Workforce
Innovation is the core of growth. At last, the mining industry, which was reluctant to embrace digitization and was focusing on mechanical force and manpower, is embracing digital technology. All the major players in the sector, who might form around
 View Details
View Details

Technology Trends for Safer & Smarter Mining Operations in 2023
Technological advancements are making the world a much more efficient and safer place. The waves of IoT (Internet of Things), Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and robotics are creating disruptions in almost
 View Details
View Details

Guide to Control Room Space Planning and Design
The control room is the epicentre of a technical setup. Ergonomics and human factor engineering play pivotal roles in the planning and design of the subject space. A foolproof system with all the elements integrated methodically will
 View Details
View Details

Role of IoT in Transforming the Mining Industry
The mining sector is dealing with increasing challenges as the world's population expands. Every industry is responding by adopting modern technologies in order to boost productivity, save costs, and maintain growth, and the mining industry is no
 View Details
View Details

Revolutionizing Pipeline Leak Detection: The Impact of Emerging Technologies
Gas system pipeline leakages can lead to catastrophic events. Timely detection and corrective measures are the only way to prevent fatal accidents that can result in human and material loss.
 View Details
View Details

Radar Systems for Maritime Surveillance on Floating Platforms
The safety and security of the vessels, coastal regions, harbors, and offshore installations are best protected by maritime surveillance systems. This surveillance is effective only if there are adept radar
 View Details
View Details

Starlink, Elon Musk’s Dream Project Commences Operation
Elon Musk has been pushing his ambitious project, Starlink for quite some time now. A state-of-the-art internet project that would connect even remote rural areas. his project under the SpaceX initiative has started functioning in selected regions in the US,
 View Details
View Details

Benefits of Automation in the Mining Sector
Automation in general has brought about inherent changes in global industries and the economy. It has made life easier for everything and everyone, and the mining sector is just one of them. he safety and efficacy of mining professionals or workers have been the major advantages that
 View Details
View Details

Critical Role of Telecom in Enabling IoT Business Solutions
The Internet of Things, or IoT, has garnered attention since the time of the digital revolution and has been gaining acceptance in different industrial fields, and the telecom industry is one of them. Internet of Things can be simply defined as the
 View Details
View Details

Autonomous Drilling Solutions In Mining
Drilling is one of the important phases in mining, the others being blasting, loading, and hauling. It is necessary to plan these processes effectively so as to avoid any sort of extra operational costs or environmental footprint. Through introducing autonomous solutions, one can ensure that the
 View Details
View Details

Challenges For Effective Leak Detection On Large-Diameter Pipelines
Pipelines are an inherent and important part of the oil and gas industry. Without them, the industry in itself is a futile option, as they can’t or won't be able to meet the demands of the market. Transportation of oil and gas through pipelines
 View Details
View Details

Aesthetix Going Green: Energy Conservation Strategies
The world is implementing measures to reduce the carbon footprint that is rapidly destroying the biosphere. As a responsible entity, we at Aesthetix have formulated exclusive working principles and production processes to maintain a reduced carbon footprint as well as limit energy
 View Details
View Details

Self-Driving Truck For Mining Fields
Self-driving vehicles have been on the radar for quite some time. Autonomous trucks are in better demand because of all the positive perks they can bring to the table. Self-driving trucks can work seven days a week for 24 hours, which means they can work all year, save a lot of money,
 View Details
View Details
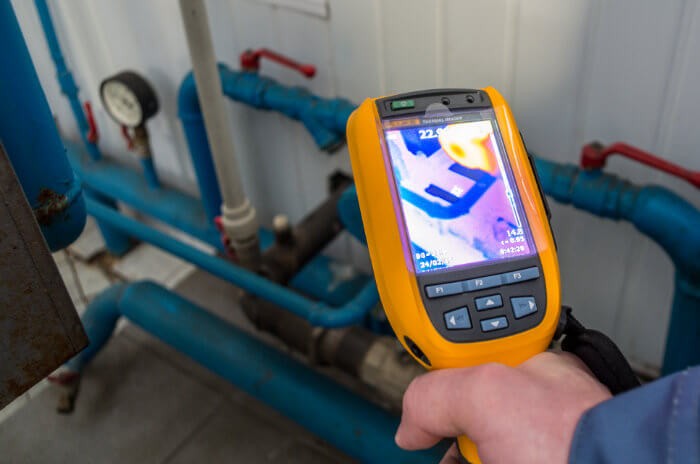

Thermal Imaging Cameras for Pipeline Leak Detection
Evaluation and monitoring the functioning of hundreds of layouts of pipelines in the oil and gas industry can be a tedious and mundane task. The number of personnel that has to be employed for the same can be quite huge and will not necessarily yield a result, which can't be sufficient
 View Details
View Details

How Radar Systems Help Offshore Platforms
Radars are a prominent element of the navigation system in airspace, marine spaces, and even on land. RADAR is the short form of "Radio Detection and Ranging." It is the use of radio wave frequencies where it is emitted and when the encountered object bounces back the
 View Details
View Details

Why Is Mining Communication Important?
Mines are one of the most hazardous working environments. The possibility of unfortunate incidents lurks behind every mine. Quick response and evacuation measures are the only ways to reduce the loss of life. These facts underscore the necessity for a seamless and efficient
 View Details
View Details

Benefits Of Unified Critical Communications For The Oil And Gas Industry
A seamless communication system is the soul of the oil and gas industry. Functioning in a highly flammable environment, constant connectivity is vital for preventing unfortunate incidents and mishaps.
 View Details
View Details

Growing Importance of Communication Technology in Mining
Long-term communication strategies form an essential part of the growth and development of the mining industry. An effective communication system has the ability to bridge the gap between the remote sites and their respective headquarters.
 View Details
View Details

Industrial Communication Solutions for the Oil & Gas Industry
The Oil & Gas Industry has been influencing everyone's lives either directly or indirectly forever. Almost every product you use has some derivative from this industry. It helps our human race to progress and ensures everything is operating
 View Details
View Details

Transforming Oil and Gas Strategies With the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to revolutionize oil and gas companies' operations completely. If handled properly, this digital technology will enable oil and gas companies to take advantage of previously inaccessible data that
 View Details
View Details

Energizing the oil and gas industry with IoT
The oil and gas industry is a volatile industry and one that plummets beyond anyone’s imagination. This highly revenue-generating activity requires a very streamlined approach to instigate the maximum revenue from selling the oil and gas industry.
 View Details
View Details

Telecommunication in the Oil and Gas Industry for Operation & Safety
The Oil and Gas industry is one of the most technologically advanced industries in the world. It relies on telecommunications to help facilitate this process. The oil and gas industry relies heavily on telecommunication networks
 View Details
View Details

Data Centralization on A Single Platform For Pipeline Leak Detection Systems
A spectrum of technologies is used for maintaining data, complying with scheduled analysis, preparing statistical reports, and implementing corrective as well as predictive maintenance. Consolidating and integrating the information from various sources
 View Details
View Details

How AI And IoT Are Used to Monitor and Detect Leaks in Pipelines
While leak detection systems (LDS) have been used by operating companies in upstream, midstream, and downstream oil and gas for decades, new regulations, rising concerns about pipeline integrity and cybersecurity
 View Details
View Details

How Digitalization can Streamline Oil and Gas Operations
The oil and gas industry is the sector that demands higher security and protection as well as being on the lookout for more advanced technology. The better technology can get the better. It is also in need of stringent measures to ensure....
 View Details
View Details
61fcf550707d2.jpg)
Fueling Ergonomics in the Oil and Gas Industry
An underrated yet extremely important facet of working in the oil & gas industry is the ergonomics of it all. It is sufficient to say that ergonomics plays an important role in any industry and sector. And for the oil & gas industry in particular, employee wellbeing factors into the productivity...
 View Details
View Details

How IoT Is Changing the Oil and Gas Industry
There are several perks associated with integrating the IoT in the oil and gas industry. IoT has used technology to facilitate the managing and controlling of sensors and devices that engage in cloud computing.It has been a great revolution for the oil and gas industry...
 View Details
View Details

All You Need To Know About Pipeline Leak Detection System
Pipeline systems are one of the most valuable and key transport support systems in any country. Having a well functioning pipeline system can immensely help various industries and sectors across the country from waterways, gas, oil, biofuel to sewage, slurry and steam.
 View Details
View Details

Ways to Perform a Perfect SAT Test
SAT or Site Acceptance Test is carried out at the buyer’s premises (plant, pipeline, platform or any other end user’s location) to ascertain the performance of the systems and equipment. The buyer’s team in association with the seller’s or original equipment...
 View Details
View Details

Why Human Factor Engineering Matters in Every Workplace
Human factors engineering is understanding the connection between human factors and the factors in the workplace that influence work. Human factors can be defined as the science of people at work. How people participate and contribute to...
 View Details
View Details

Fatigue and Stress Management Study
The purpose of this study is to explain the minimum requirements of conducting fatigue risk management study for selected ADNOC Gas Processing sites and develop a system of managing, monitoring and reporting of fatigue to increase the productivity of the workers.
 View Details
View Details

How Drone Inspections Can Be A Game-Changer For Oil & Gas Industry
Conventional methods of inspecting oil and gas assets are risk-filled and time-intensive. Sophisticated drones are the new alternative to inspect hard-to-reach places, eliminating risks and saving a lot of time as well as money.....
 View Details
View Details
